Within a couple of months, the COVID-19 (Novel Coronavirus) that emerged from the city of Wuhan has spread across China and the world. It bears some resemblance to SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome), though less lethal but more contagious. To curb the spread of the Coronavirus epidemic, the Chinese government issued a strict travel ban on 24th January.
This will hurt China’s macroeconomy as retail and commerce activities slowed sharply, thereafter. The Chinese Spring Festival break was extended to early Feb and most companies tried to resume operation on 10th February. However, social and production activities in China are still limited.
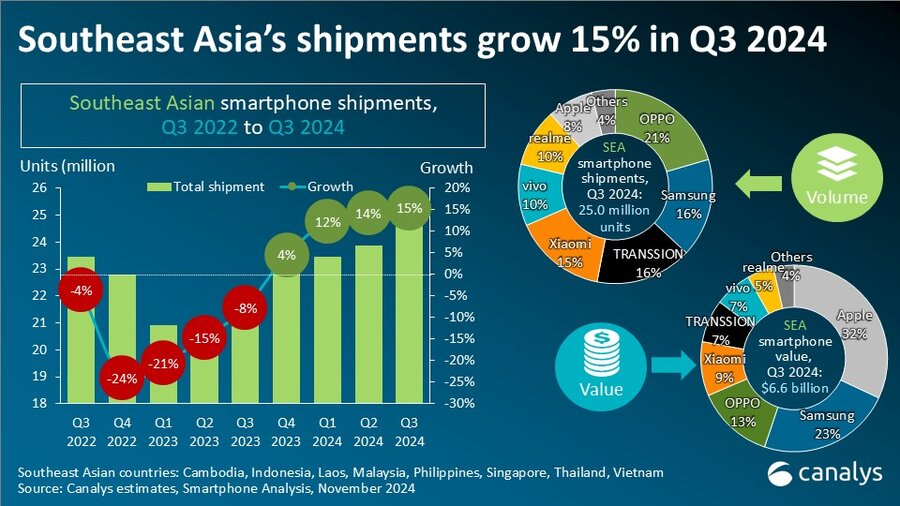
Q1 China smartphone sales will drop more than 20%
Commenting on impacts of the nCoV on the overall Chinese smartphone market, Brady Wang, Associate Director at Counterpoint Research, said, “Demand-wise, we see the market impacted severely. We estimate more than a 50% YoY decline in offline smartphone sales during the lock-down period. Therefore, we have lowered our sales forecast 20% for Q1.
The situation may worsen and we may lower our forecast even more depending on the February sales. The plummet in Q1 is likely to generate a surge in channel inventories and further influence shipments and new products launches through Q2.”
Commenting on influence on sales of smartphone OEMs, Flora Tang, Research Analyst at Counterpoint Research, said, “Huawei group is likely to suffer as China has accounted for over 60% of its total smartphones sales. OPPO and Vivo will also be impacted because of their greater reliance on offline sales channels. The influence on sales of Xiaomi, OnePlus and Realme will likely be less severe as they are more online-centric and overseas-focused.”
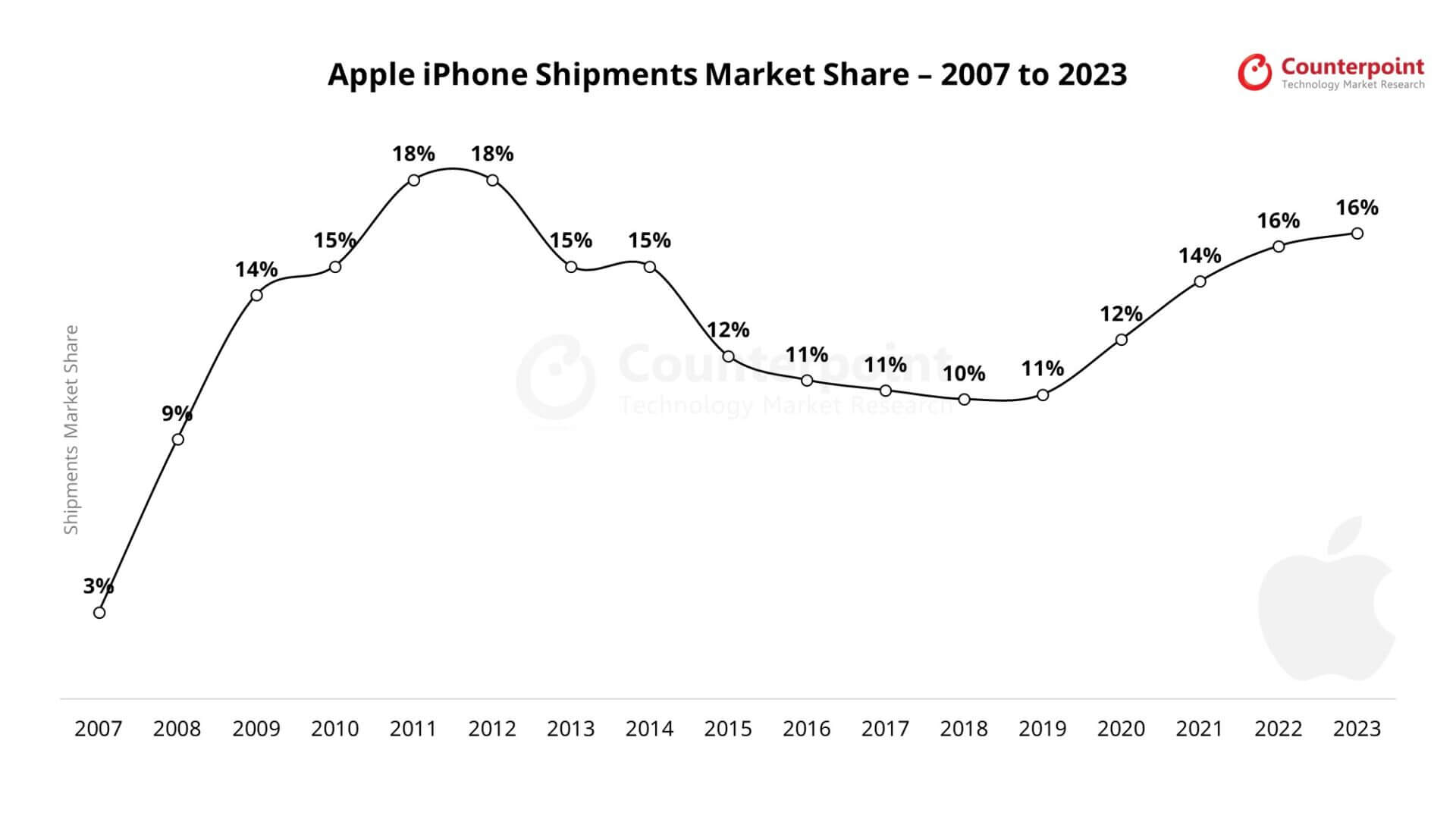
Mengmeng Zhang, Research Analyst at Counterpoint Research, added, “Apple has announced a shutdown of its offline stores across China until 15th February. We estimate that this will bring a sales loss of about one million units of iPhones.
Apple’s new product development plans will also be affected as engineers from the USA and Taiwan cannot travel to China. The iPhone SE2 set for a late March launch is likely to have troubles in ramping up volume due to the insufficient labour force in Foxconn’s Zhengzhou factory.”
Commenting on potential influence on the supply side, Ethan Qi, Senior Analyst at Counterpoint Research, said, “We expect new device launches, planned for the first half, will be materially impacted because factories in China will not function properly. Though most electronic manufacturers have resumed operation since 10th February, they will be operating slowly and cautiously. We do not expect them to resume full capacity until at least the end of February.
This will also influence components sourced from China such as displays from BOE, CSOT and semiconductors from YMTC. However, as the end market demands also drop dramatically, we haven’t seen evidence of supply shortages caused by a slowdown in manufacturing yet. We will continue to observe how this situation will evolve.”
Global smartphone sales to drop 5% in 1Q 2020
“Overall, we think the virus will be contained in March.” Tom Kang, Research Director with Counterpoint Research, said, “However, it may take two more months for commerce activities in China to fully go back to normal. We expect negative growth in Q1 and Q2 2020, in both China and global smartphone markets.
Some smartphone brands have factories in Wuhan, and Hubei province. Also some Chinese OEMs already have shortages in some components. So global sales may show 5-6% negative growth in Q1. Some sales may be shifting to Q3 this year but not all the demands will be shifted for the mismatch between old devices and new devices. We had previously expected the global smartphone market to see YoY growth in CY2020 but now it will likely be flat.”